Understand
Your Roofing Contractor
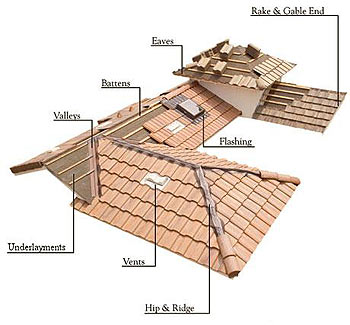
Roofers Alphabet- Commonly used roofing terms
Asphault
Bituminous; one can apply this to materials for roofing in order to make them waterproof
Back Surfacing
Thin mineral layer on the underside of shingles in order to prevent sticking
Blister
Bubbles that can occasionally appear on asphalt roofing surfaces once installed
Built-up roof
Roof with little to no slope containing numerous layers of ply sheets and asphalt
Caulk
Material which is used to close any joint with asphalt cement or mastic cement to keep it from leaking
Class "A"
The top-level of fire-resistance roofing ratings, as determined by ASTM E-108. This rating means that a roof can undergo and hold up through critical exposure to flames in the case that the fire begins outside of a building.
Class "B"
Also determined by the ASTM E-108, is the second highest rating which means that a roof and its materials can withstand medium or moderate fire exposure from a blaze that starts outside of a building.
Class "C"
The lowest fire-resistance rating, means the roof can handle only mild exposure to flames that occur or begin outside of a building.
Concealed Nail method
Nails will not be exposed to weather, but instead are placed and secured under the roofing and then covered with a course of cement.
Condensation
Occurs when water changes from vapor (or gas) to liquid, usually when the air is warm or moisture-heavy and meets a cool surface.
Coverage
Refers to how much weather protection is present in the roofing materials
Deck or sheathing
The surface where roofing materials are attached, typically OSB (oriented strand board) or plywood
Dormer
Small section of a structure that projects from a roof with a low slope; it typically has a window
Downspout
Roof gutter pipe that carries water away and down
Drip Edge
Material in the shape of an L, normally made of metal, placed in line with the edges of the roof to keep water from dripping onto the siding, deck, or eaves
Eave
The lower, horizontal lip of a roof with a slope
Edging Strips
Used when replacing or altering wood shingles with asphalt shingles – pieces of wood are nailed along the edges and rakes once the wood shingles have been cut back to create sound edges
Fascia
On a cornice’s outermost edge; it is usually a level board, face, or band
Felt or underlayment
Provides another level of roof deck protection, made from an asphalt-soaked sheet (sometimes referred to as tar paper)
Flashing
Roll roofing or metal pieces usually placed at projections, corners, or intersections (chimneys, dormers, valleys, or walls, for example) of a roof to keep water from dripping into the building
Fire Ratings
Comprised of Classes A, B, and C – are a method of categorizing the fire impermeability or resistance of roofing materials. Class A is the highest of the fire ratings, and has the most resistance to outside flames.
gable
Top section of sidewall which comprises part of an arrow point on a sloped roof edge.
granules
Cover the exposed areas of roofing materials made with asphalt. Granules are typically covered in ceramic and come in various colors.
Gutter
Pipe and collection area that transports water through the eaves and a downspout.
Insulation
Ranges from 1/2 inch to 6 inches, typically a board secured with metal fastenings. If there are multiple layers of insulation applied, the next one is secured with some kind of adhesive.
Interlocking Shingles
Provide wind resistance with individual shingles mechanically secured together.
Louvers
Slatted pieces placed on the soffit or gable in order to air out the area underneath a roof deck and balance the temperature of the air and the moisture level.
Oriented Strand Board
(or OSB) is a popular replacement for plywood roof panels, crafted of thin pieces of wood placed long-ways and across in layers, then cemented with resin glue. They are usually 4 feet by 8 feet.
Overhang
The section of a roof that juts out beyond the outside walls of any structure or building.
penetrations
Anything that is considered to be “penetrating” the deck of a roof, such as a chimney, vents, stacks, or pipes.
Pitch
The size of the roof’s incline, which is expressed as rise by the span, both in feet.
Rafters
Support the framing that is attached to the roof deck.
Rake
The roof’s sloped edge over the wall.
Ridge
The top of the meeting point of any two sloped surfaces on the roof.
Sheathing
Used to coat a building or structure, and is typically comprised of sheet materials or boards which are affixed to rafters.
Soffit
The finished bottom side of eaves.
Slope
Refers to a roof’s “rise” by its horizontal “run”, both in inches; for example, a roof that has a 3-in-10 slope rises 3 inches for every 10 inches across.
Square
The most typical measurement for a roof’s area. A Square in roofing is 10 feet x 10 feet, or 100 square feet.
Truss
An unalterable, fabricated material that serves as a companion to rafters in modern or more recent buildings and houses. They usually serve a particular purpose, which is why they cannot be changed or cut.
Underlayment
Ensures further protection for a roof deck; it is placed on an uncovered deck prior to installing shingles, and is usually made of tar paper (which is saturated with asphalt).
Valley
The specific angle that occurs at the junction of two sloped roof sections.
Vapor Retarder
A substance specifically intended to limit water passing through a wall or roof.
Vent
Relates to anything placed on a roof, soffit, or gable in order to keep the underneath areas of a roof deck properly ventilated.
© platteriverroofing 2020
